Visual defects
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Degeneration of the central retina, or macula, is a visual defect that mainly affects people over the age of 50. It is characterized by a reduction in central vision, leading to profound or even total loss of vision.
Early detection and regular monitoring can limit the progression of the disease.
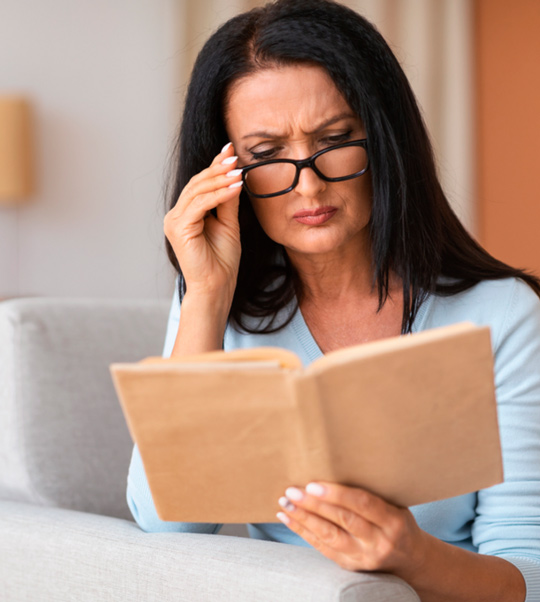

Types of AMD
The symptoms
There are two types of AMD that have the same impact on the central vision of the retina:
- Dry (atrophic) form
The dry form is the most widespread. It is distinguished by its slow evolution. To date, there is no truly effective treatment for it. Dietary supplements can slow retinal degeneration (Omega 3, antioxidants). - The wet (exudative) form
The wet form is characterized by the formation of new blood vessels deep inside the retina, which damage central vision. Anti-VEGF injections can limit or destroy these new vessels.

Solutions
Treatments
To date, there is only one treatment for exudative AMD, which involves injecting anti-VEGF to limit or destroy the formation of new blood vessels deep inside the retina.
In both cases, early detection and regular monitoring can limit the progression of the disease. Vision rehabilitation can also help maintain independence when irreversible vision damage has occurred.

Make an appointment at the clinic
Appointments can be booked directly on our website or via the OneDoc app.
Appointments for laser surgery can only be made via our WhatsApp line.
In case of emergency, please contact us directly on 022 365 18 80
